In this blog post, I’ll dive into the DAX TREATAS function by first showing how to create a virtual relationship between two tables using TREATAS and then move on to show how we can simplify a filtering expression using the TREATAS function.
Virtual Relationship using TREATAS
The Best practice to move a filter from one table to another is to create a physical relationship between the two tables involved. What if the relationship doesn’t exist, is there a way to create virtual relationship between these two tables to mimic physical relationship so that the user thinks there is a relationship in place, even if there is none? Using DAX TREATAS function, you can create a virtual relationship between tables that mimic physical relationship. This technique is useful whenever a relationship does not exist between the tables involved.
In order to show how to create a virtual relationship between two tables such the Reseller and Sales tables, I have deleted the physical relationship existing between these two tables using data from Adventure Works DW 2020 which can be seen from the data model below
Without any physical relationship between the Reseller and Sales tables, let look at the amount of sales by country using DAX Studio
EVALUATE
SUMMARIZECOLUMNS(
Reseller[Country],
"Sales Amount",[Sales Amt]
)
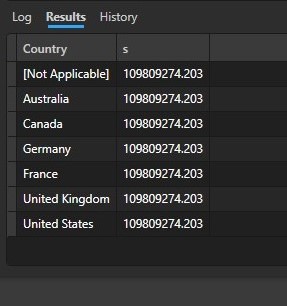
From the preceding figure we see that the sum of sales amount is the same for all the countries involved because there no relationship between the two tables.
Using TREATAS, it applies the result of a table expression as filters to columns from an unrelated table and is defined by the syntax below
TREATAS(table_expression, <column>[, <column>[, <column>[,…]]]} )
With the TREATAS function, I can create a virtual relationship between the two tables to propagate the filter context from Reseller to Sales and it is given by the code below,
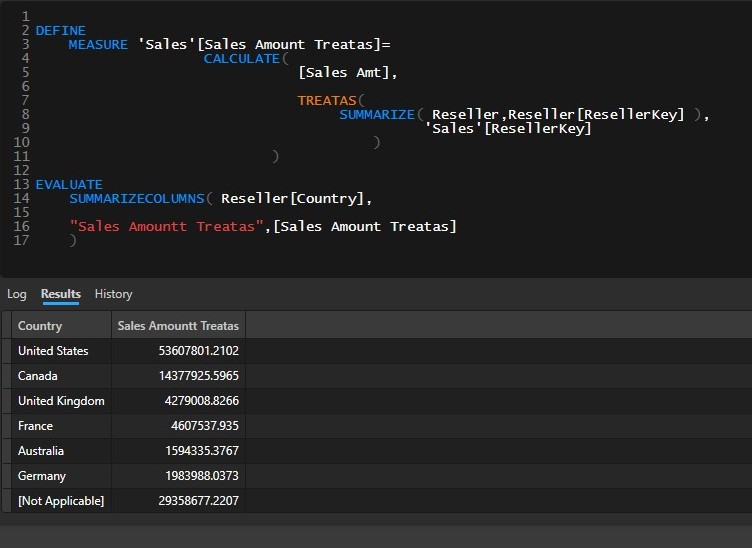
TREATAS connects the two tables using the ResellerKey column, and the preceding figure shows that the amount of sales is filtered by Country, even though there is no physical relationship existing between the two tables.
Let now create a physical relationship between the Reseller and Sales tables using the ResellerKey column in power BI as below to see if it will produce the same result
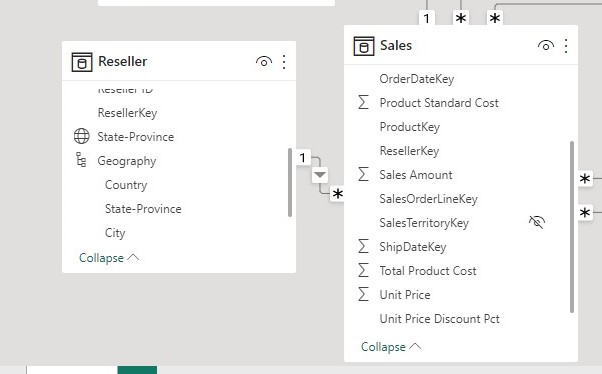
With the physical relationship between the tables created, let check if we will get the same result for the amount of sales filtered by country as that of the virtual relationship.
Result of the Data model with physical relationship.
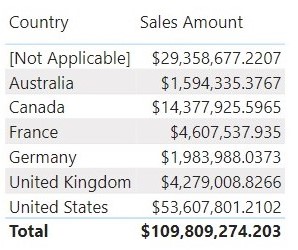
Result of the Data model with virtual relationship.
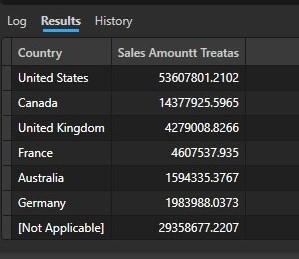
We can see from the above figures that result of the Data model with physical relationship and that of Data model with virtual relationship produce the same results.
Filtering Values Using TREATAS
In this section of the post I will be filtering values using the TREATAS function. Before we start using TREATAS to filter values, we need to create two calculated columns since the columns needed for the filtering are not part of data model.
Let add two calculated two columns name Year and Month Num to the date table which contain the year and the number representing the month.
Year = YEAR([Date])
Month Num = MONTH('Date'[Date])
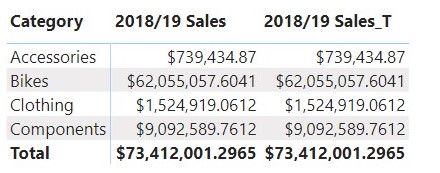
With the calculated columns created, let now create two measures 2018/19 Sales and 2018/19 Sales_T which filter the amount of sales for 2018 or 2019 using the FILTER and TREATAS function respectively.
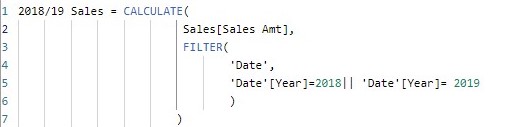
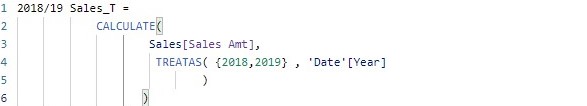
Let now use the report canvas to display the values for the two measures created
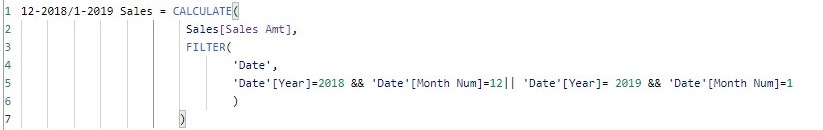
Continuing the filtering examples, let create additional two measures 12-2018/1-2019 Sales and 12-2018/1-2019 Sales_T which filter the amount of sales for 12/2018 or 1/2019, using the filter function and TREATAS function respectively and where 1 and 12 represent months. For instance 1=January.
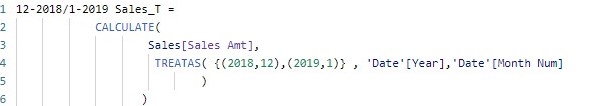
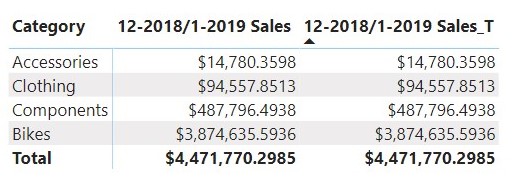
Let now use the report canvas to display the values for 12-2018/1-2019 Sales and 12-2018/1-2019 Sales_T
Conclusion
In this post we’ve seen that the TREATAS function is an important function which can be used to simplify filtering expressions and also used to create a virtual relationship between two tables.